Outline of the Fukuoka City Council
Japan’s Local Government System
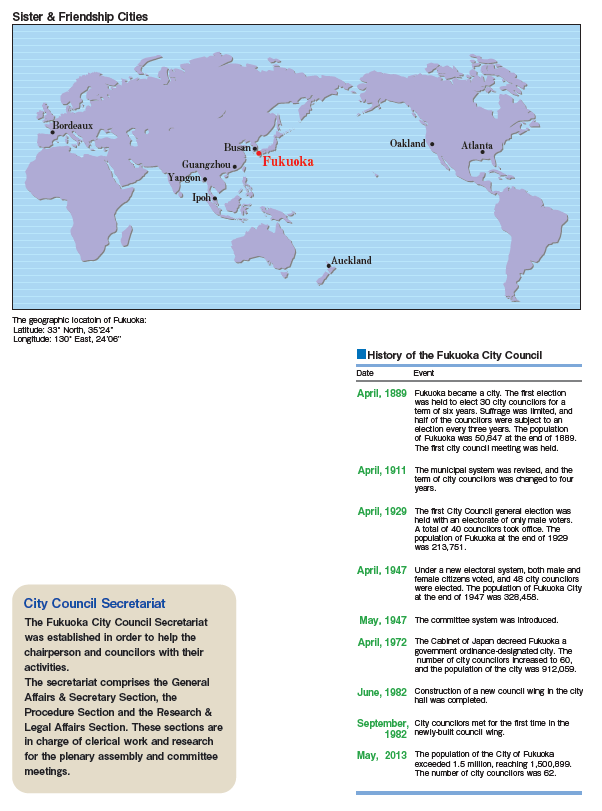
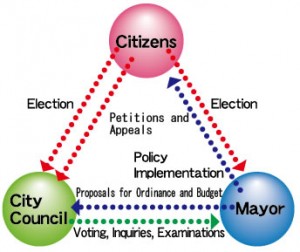
In Japan’s local government system, prefectures and municipalities oversee local affairs in accordance with the Japanese Constitution. For example, municipalities focus on public services such as education, social welfare and water supply and sewage services. On the other hand, prefectural governments are responsible for multiple municipalities over a wider area. The City of Fukuoka, however, is authorized to perform some prefectural-level responsibilities, because the city is a government ordinance-designated city with a population of over 500,000. This status means the city is entitled to greater authority than other municipalities.Local public entities comprise a decision-making assembly or council and the leader of the executive body. The assembly has the overall authority to make decisions on agenda items submitted to the assembly for discussion. The leader’s role is to instruct and supervise government employees to carry out what has been decided by the assembly. Assembly members and the leader are directly elected by the electorate, and better governance is ensured through the separation of powers, mutual checks and cooperating with each other.
Citizens and the City Council
Elections
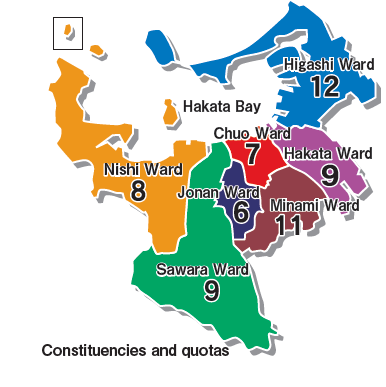
Citizens aged 18 years and older have the right to vote in city council elections. Citizens aged 25 years and older can run for council. The Fukuoka City Council consists of 62 members elected from seven electoral constituencies that correspond with the city’s administrative wards, each of which has a set quota of councilors to elect.
Petitions and Lobbying
Citizens can make requests about public administration to the City Council through petitions. This process can be done either through a city councilor or through a direct lobby to the City Council, but both are submitted in writing. The contents of petitions are reviewed by a council committee before the Council itself chooses whether to adopt the petition or not. Petitioners are then notified of the outcome, and adopted petitions are passed to the relevant department, such as the Mayor, to be implemented.
Petitions sent directly to a committee by lobbyists are distributed to each committee member, but a decision on whether or not to adopt a proposal will not be issued.
Direct Requests
If a citizen obtains a specific number of voters’ signatures, they may submit a request to dissolve the City Council or to dismiss a councilor.
Observing a City Council Session
Council sessions are open to the public for anyone to observe. Members of the public can also observe committee meetings.

Powers of the City Council
The City Council has the authority to make resolutions, to conduct inquiries and to perform audits etc. to ensure that it properly performs its duties as representatives of the people. The Council carries out the following:
Resolutions (Legislative Powers)
The most fundamental duty of the City Council is to make decisions on important matters such as ordinance and budgets.
Elections
The chairperson, vice chairperson and members of the Election Management Committee are elected by the City Council.
Approvals
The City Council decides whether to approve deputy mayors and city auditors appointed by the mayor.
Inspections and Audits
The City Council has the power to inspect official documents and request audits.
Inquiries
The City Council can perform investigations into city administration and, when necessary, can summon related persons for testimony or request the submission of records.
Submission of Written Opinions
The City Council can submit written opinions concerning the city’s public interest to relevant administrative organs of the national and prefectural governments, such as the National Diet.
Structure of the City Council
City Councilors
Fukuoka City Council is made up of 62 councilors. Councilors serve for a term of four years.
Chairperson and Vice Chairperson
The chairperson and vice chairperson of the City Council are elected from its members. The chairperson of the City Council represents the Council and presides over its meetings. The vice chairperson takes over the duties of the chairperson in his/her absence.
Political Factions
There are several political factions formed by councilors who share similar opinions and ways of thinking in the Fukuoka City Council.
Activities of the City Council during an Regular Session
| Plenary Assembly |
|
| Committees |
|
| Plenary Assembly |
|
City Council Meetings
There are two types of meetings held in the City Council, both of which are convened by the mayor: regularly scheduled sessions and emergency sessions when necessary. Both sessions must finish within the predetermined period, during which, the plenary assembly as well as committee meetings are held to examine and adopt proposed items on the agenda. Regular sessions are held four times a year: in either February or March, and in June, September and December. In principle, the City Council has to reach a conclusion on items on the agenda by the due date. However, if they are unable to do so, they may convene committee meetings to continue examining the item.
Plenary Assembly
The plenary assembly involves all councilors, where they make the final decisions on all items on the agenda. A session cannot be convened without at least half of all councilors present. A majority of votes is required to make decisions.
Committees
Committees of a small number of people are established for the technical review of proposed legislation. There are three types of committees: standing committees, special committees and City Council management committees.
Standing Committees
There are five standing committees in the City Council. Each city councilor belongs to one of the five committees.

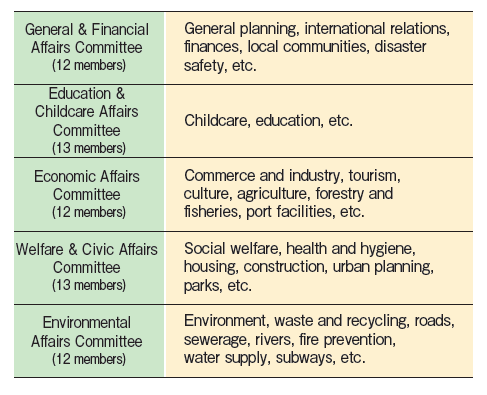
Special Committees
Special committees are set up to review initial budgets and account settlements. They are also set up when issues arise that require special examinations or inquiries.
City Council Management Committee
The City Council Management Committee is convened to discuss matters relating to the order of the agenda and the procedure of meetings to ensure smooth management of the City Council. The committee consists of 13 councilors.